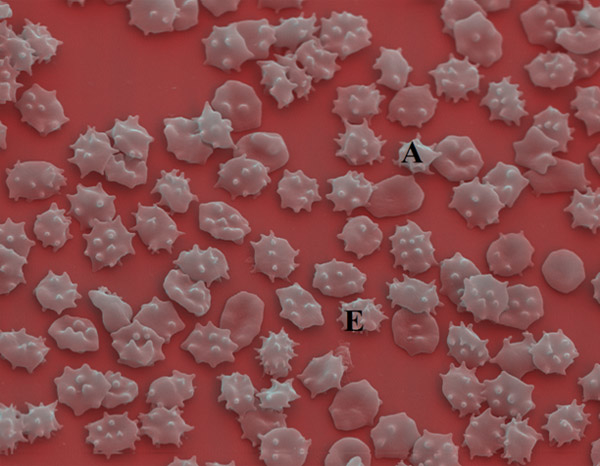
Figure 1
Chorea-acanthocytosis: acanthocytic (A) and echinocytic (E) deformation of RBCs.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2010.13039
The Example of Chorea-Acanthocytosis

Figure 1
Chorea-acanthocytosis: acanthocytic (A) and echinocytic (E) deformation of RBCs.
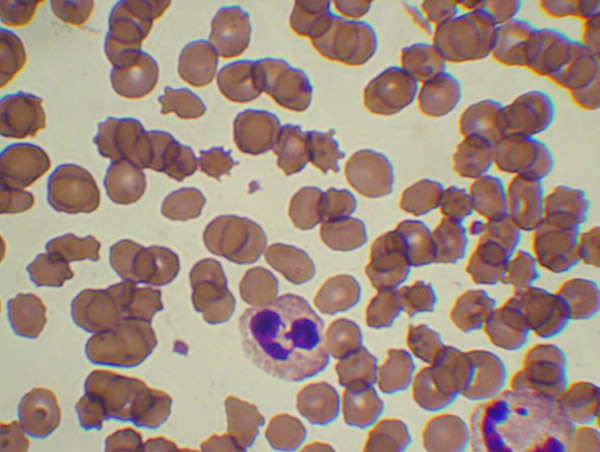
Figure 2
ChAc: peripheral blood smear: differentiating echino-/acanthocytes.
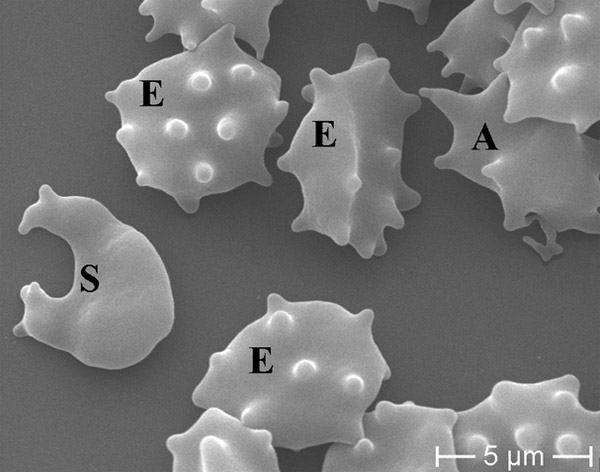
Figure 3
ChAc: schizocyte (S), acanthocytes (A) and echinocytes (E) in concomitance.
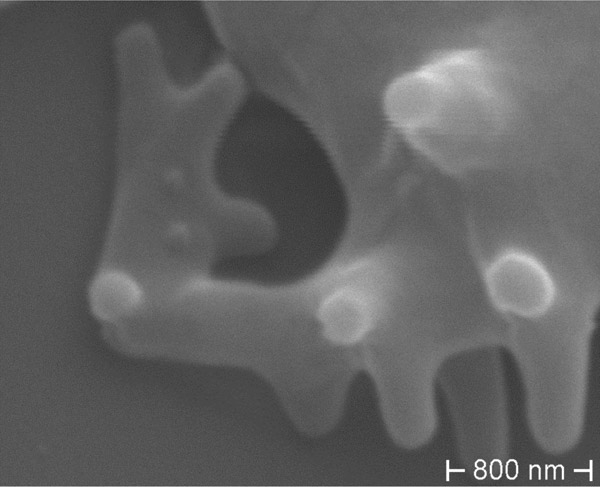

Figure 4
ChAc: Gross deformation of RBC membrane in acanthocyte.
EDTA-blood sample from an advanced genetically proven Chorea-acanthocytosis (ChAc) clinical case with severe choreo-athetoid movement disorders, orofacial dyskinesia and dementia is fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyd and stored at room temperature for 24 h in Sörensen solution. After three washing procedure (centrifugation in bidest. H2O), the solution is dehydrated in increasing concentrations of acetone (20, 40, 60, 80, 95 and 100%; 10 min each), placed on Poly-l-lysine coated 6 mm coverslips and air dried for 2 h. Platin coating was performed with a Balzers SCD 004 sputter coater and visualised with a Scanning Electron Microscope Jeol JSM 840, with 15.0 kV accelerating voltage, magnification 1400 × (fig. 1), 6000 × (fig. 3) and 35 000 × (fig. 4), 13 000 (fig. 5c), 7500 × (fig. 6c). The light-microscopic images (fig. 2, 5a,b, 6a,b) were recorded with a Zeiss Axiovert 200 M, camera Sony DSC-S85, standard preparation and stain [15] from EDTA blood. Control blood was derived from an hepatocellular carcinoma suffering patient.
I thank Dr V. Saglini and Dr Gianantonio Rosti for reviewing the present paper. I thank the patient and her family for providing me the blood to investigate.
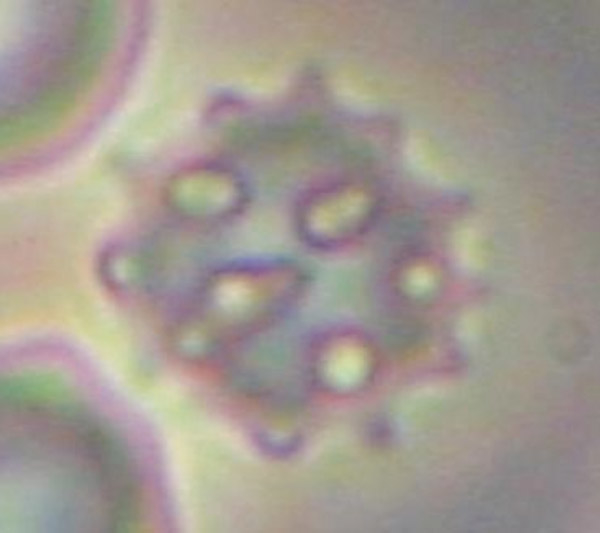
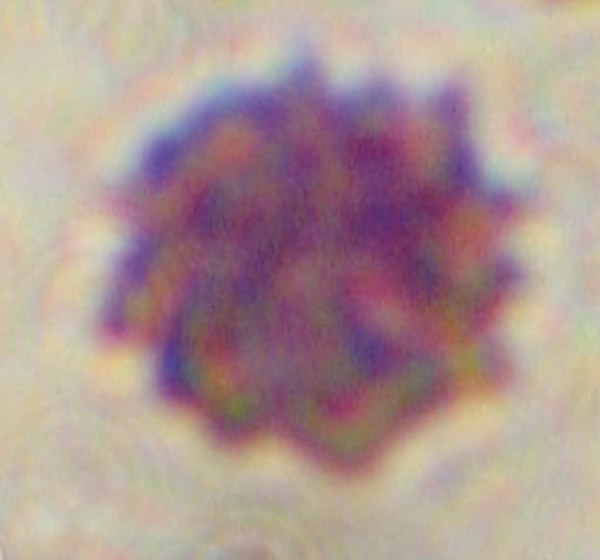
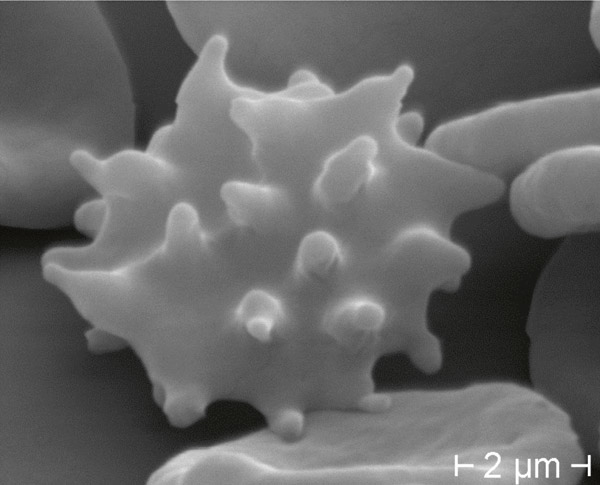
Figure 5
Echinocyte in control blood: numerous spiculae regularly distributed in living specimen (DIC 945 x) (a), standard staining (BF 1000 x oil) (b), and Scanning Electron Microscope (c).
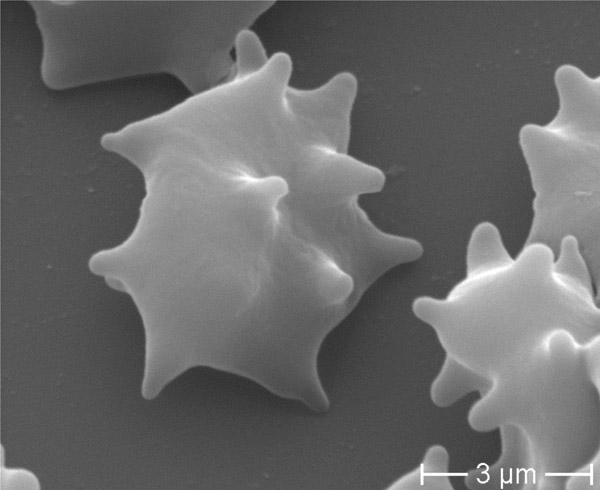
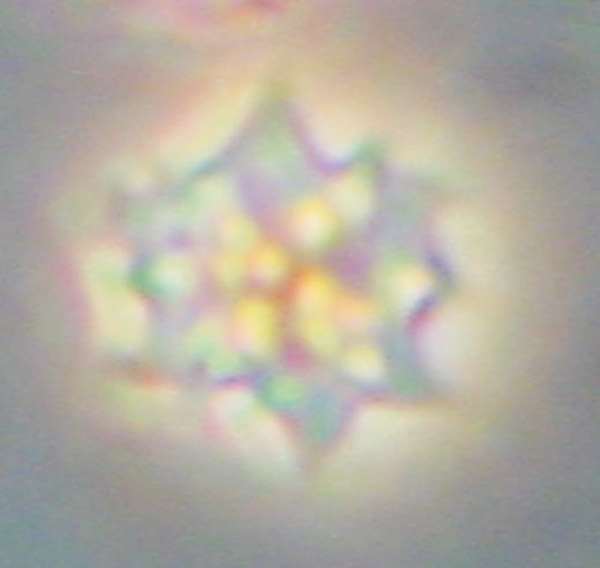


Figure 6
Acanthocyte in ChAc: fewer irregularly distributed spiculae, in living specimen (DIC 945 x) (a), standard staining (BF 1000 x oil) (b), and Scanning Electron Microscope (c).
1 Danek A. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes, Springer Verlag, 2005: 5–7.
2 Walker RH, Saiki S, Danek A. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes, A Current Overview. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes II, Springer Verlag, 2008: 3–4.
3 Ichiba M, Nakamura M, Sano A. Neuroacanthocytosis update, Brain Nerve. 2008;60(6):635–41.
4 Hardie RJ, Pullon HW, Harding AE, et al. Neuroacanthocytosis. A clinical, haematological and pathological study of 19 cases. Brain. 1991;114(1A):13–49.
5 Huppertz HJ, Kröll-Seger J, Danek A, et al. Automatic striatal volumetry allows for identification of patients with chorea-acanthocytosis at single subject level. J Neural Transm. 2008;115(10):1393–400.
6 Bosman GJ, Horstink MW, de Grip WJ. Erythrocyte membrane abnormalities in neuroacanthocytosis. Evidence for a neuron-erythrocyte axis. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes, Springer Verlag, 2005: 153–60.
7 Perrin J, Georges A, Morali A, et al. Acanthocytes et hypercholesterolemia. Ann Biolo Clin. 2008;66(5):56972.
8 Bosman GJ, De Franceschi L. Neuroacanthocytosis-related changes in erythrocyte membrane organization and function. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes II, Springer Verlag, 2008: 133–42.
9 Marson AM, Bucciantini E, Gentile E, Geda C. Neuroacanthocytosis: clinical, radiological and neurophysiological findings in an Italian family, Neurol Sci. 2003;24(3):188–9.
10 Galey WR, Evan AP, Van Nice PS, et al. Morphology and physiology of the McLeod erythrocyte. I. Scanning electron microscopy and electrolyte and water transport properties. Vox Sang. 1978;34(3):152–61.
11 Lichtman M, Bentler E, Kipps TJ, et al. Williams Hematology, 7th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2005:369–82.
12 Reinhart WH, Chien S. Red Cell Rheology in Stomatocyte-Echinocyte Transformation: Roles of Cell Geometry and Cell Shape. Blood. 1986;4:1110–8.
13 Wong P. A Basis of Echinocytosis and Stomatocytosis in the Disc-sphere Transformations of the Erythrocyte, J Theor Biol. 1999;196(3):343–61.
14 Mrowietz C, Hiebl B, Franke RP, et al. Reversibility of Echinocyte Formation after Contact of erythrocytes with various Radiographic Contrast Media. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2008;39(1–4):281–6.
15 Schwarz S, Deuticke B, Haest CW. Passive Transmembrane Redistributions of Phospholipids as a Determinant of Erythrocyte Shape Change. Studies on Electroporated Cells. Mol Membr Biol. 1999;16(3):247–55.
16 O’Connor BH. A Color Atlas and Instruction Manual of Peripheral Blood Cell Morphology, William & Wilkins, 1984: 3–5.